2.2 Wind Direction
- wind
vanes
- uv
and uvw systems
- transducers
Wind
direction is generally defined as the orientation of the wind vector in the
horizontal.
Wind
direction for meteorological purposes is defined as the direction from which
the wind is blowing, and is measured in degrees clockwise from true north.
Wind direction determines the transport direction of a plume or puff in air
quality modeling applications.
The standard deviation of the wind direction,
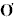 A , or the standard
deviation of the elevation angle,
A , or the standard
deviation of the elevation angle, 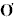 E , may also be used, in conjunction with wind speed, to derive the
atmospheric stability category (Section 6.4). Wind direction may be measured
directly using a wind vane (Section 2.2.1) or may be derived from
measurements of wind speed components (Section 2.2.2).
E , may also be used, in conjunction with wind speed, to derive the
atmospheric stability category (Section 6.4). Wind direction may be measured
directly using a wind vane (Section 2.2.1) or may be derived from
measurements of wind speed components (Section 2.2.2).
2. PRIMARY METEOROLOGICAL VARIABLES
2.1 Wind Speed
2.1.1 Cup Anemometers
2.1.2 Vane-oriented and Fixed-mount Propeller Anemometers
2.1.3 Wind Speed Transducers
2.2 Wind Direction
2.2.1 Wind Vanes
2.2.2 U-V and UVW Systems
2.2.3 Wind Direction Transducers
2.2.4 Standard Deviation and Turbulence
Data
2.3 Temperature and Temperature Difference
2.3.1 Classes of Temperature Sensors
2.3.2 Response Characteristics
2.3.3 Temperature Difference
2.3.4 Sources of Error
2.4 Humidity
2.4.1 Humidity Variables
2.4.2 Types of Instrumentation
2.5 Precipitation
2.6 Pressure
2.7 Radiation
2.8 Recommendations











