6.2 Wind Direction and Wind Speed
This
section provides guidance for processing of in situ measurements of wind
direction and wind speed using
conventional in situ sensors; i.e., cup and propeller anemometers and wind
vanes. Guidance for processing of upper-air wind measurements obtained with
remote sensing platforms is provided in Section 9. Recommendations are
provided in the following for processing of winds using both scalar
computations (Section 6.2.1) and vector computations (Section 6.2.2). Unless
indicated otherwise, the methods recommended in Sections 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 employ single-pass
processing; these methods facilitate real-time processing of the data as it
is collected. Guidance on the treatment of calms is provided in Section
6.2.3. Processing of data to obtain estimates of turbulence parameters is
addressed in Section 6.2.4. Guidance on the use of a power-law for
extrapolating wind speed with height is provided in Section 6.2.5. The
notation for this section is defined in Table 6-2.
Table 6-1
Notation
Used in Section 6.2 |
|
Observed Raw Data |
| ui | signed
magnitude of the horizontal component of the wind vector (i.e.. the
wind speed) |
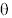 i i | azimuth angle
of the wind vector, measured clockwise from north (i.e. the wind
direction) |
| Wi | signed
magnitude of the vertical component of the wind vector |
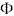 i i | elevation
angle of the wind vector (bivane measurements) |
| N | number of
valid observations |
|
Scalar wind computations |
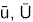 | scalar mean
wind speed |
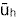 | harmonic mean
wind speed |
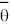 | mean azimuth
angle of the wind vector |
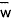 | mean value of
the vertical component of the wind speed |
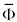 | mean elevation
angle of the wind vector |
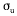 | standard
deviation of the horizontal component of the wind speed |
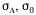 | standard
deviation of the azimuth angle of the wind |
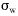 | standard
deviation of the vertical component of the wind speed |
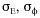 | standard
deviation of the elevation angle of the wind |
|
Vector wind computations |
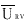 | resultant mean
wind speed |
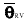 | resultant mean
wind direction |
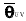 | unit vector
mean wind direction |
| Ve | magnitude of
the east-west component of the resultant vector mean wind (positive
towards east) |
| Vn | magnitude of
the north-south component of the resultant vector mean wind
(positive towards the north) |
| Vx | magnitude of
the east-west component of the unit vector mean wind |
| Vy | magnitude of
the north-south component of the unit vector mean wind |
| x, y, z | stadard
right-hand-rule coordinate system with x-axis alighned towards |
















