6.4.1 Turner's method
Turner
[34] presented a method for determining P-G stability categories from
data that are routinely collected at National Weather Service (NWS)
stations. The method estimates the effects of net radiation on stability
from solar altitude (a function of time of day and time of year), total
cloud cover, and ceiling height. Table 6-4 gives the stability class (1=A,
2=B,...) as a function of wind speed and net radiation index. Since the
method was developed for use with NWS data, the wind speed is given in
knots. The net radiation index is related to the solar altitude (Table 6-5)
and is determined from the procedure described in Table 6-6. Solar altitude
can be determined from the Smithsonian Meteorological Tables [36].
For EPA regulatory modeling applications, stability categories 6
and 7 (F and G) are combined and considered category 6.
Table 6-6
Procedure for Determining the Net Radiation Index |
1.
If the total cloud1 cover is 10/10 and the ceiling is
less that 7,000 feet,
use net radiation index equal to 0 (whether day
or night) |
| 2.
For nighttime: (from one hour before sunset to one hour after
sunrise): |
| a.
If total cloud cover 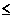 4/10,
use net radiation index equal to -2. 4/10,
use net radiation index equal to -2. |
| b.
If total cloud cover > 4/10, use net radiation index equal to -1. |
| 3.
For Daytime |
| a.
Determine the insolation class number as a function of solar
altitude from Table 6-5 |
| b.
If total cloud cover 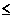 5/10,
use the net radiation index in Table 5/10,
use the net radiation index in Table
6-4 corresponding to the isolation class number. |
| ©
If cloud cover > 5/10, modify the insolation class number
using
the following six steps. |
| | 1.) Ceiling
< 7,000 ft, subtract 2 |
| | 2.) Ceiling 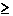 7,000
ft, but < 160,000 ft, subtract 1 7,000
ft, but < 160,000 ft, subtract 1 |
| | 3.) Total
cloud cover equal to 10/10, subtract 1. (This wil
only apply to ceiling 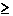 7,000
ft since cases with 10/10 7,000
ft since cases with 10/10
coverage below 7,000 ft are considered in
item 1
above.) |
| | 4.) If
insolation class number has not been modified by
steps 1.), 2.) or 3.) above, assume
modified class
number equal to insolation class
number. |
| | 5.) If
modified insolation class number is less than 1, let it
equal to 1. |
| | 6.) Use the
net radiation index in Table 6-4 corresponding to the modified
insolation class number. |
1
Although Turner indicates total cloud cover,
opaque cloud cover is
implied by Pasquill and is preferred; EPA recommended
meteorological
processors, MPRM and PCRAMMET, will accept
either. |
















