6.2.4 Turbulence
6.2.4.1 Estimating 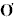 E from
E from 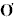 w
w
Applications
requiring the standard deviation of the elevation angle of the wind (e.g.,
see Section 6.4.4) should use the following approximation:

where
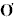 E
is the standard deviation of the elevation angle of the wind (radians)
E
is the standard deviation of the elevation angle of the wind (radians)
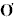 w is the standard
deviation of the vertical component of the wind speed (m/s)
w is the standard
deviation of the vertical component of the wind speed (m/s)
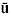 is the scalar
mean wind speed (m/s).
is the scalar
mean wind speed (m/s).
Weber
et. al. [30] reported good performance for an evaluation using data
measured at the Savannah River Laboratory for wind speeds greater than 2
m/s. In a similar study, Deihl [31] reported satisfactory performance
for wind speeds greater than 2 m/s. In the Deihl study, the performance
varied depending on the overall turbulence intensity. It is concluded from
these studies that 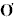 E
is best approximated by
E
is best approximated by 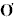 w/
w/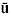 when wind speeds are greater than 2 m/s, and
when wind speeds are greater than 2 m/s, and 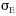 is u greater than 3 degrees.
is u greater than 3 degrees.
6. METEOROLOGICAL DATA PROCESSING
6.1 Averaging and Sampling Strategies
6.2 Wind Direction and Wind Speed
6.2.1 Scalar Computations
6.2.2 Vector Computations
6.2.3 Treatment of Calms
6.2.4 Turbulence
6.2.5 Wind Speed Profiles
6.3 Temperature
6.3.1 Use in Plume-Rise Estimates
6.3.2 Vertical Temperature Gradient
6.4 Stability
6.4.1 Turner's method
6.4.2 Solar radiation/delta-T (SRDT) method
6.4.3
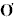 E method
E method
6.4.4 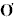 Amethod
Amethod
6.4.5 Accuracy of stability category estimates
6.5 Mixing Height
6.5.1 The Holzworth Method
6.6 Boundary Layer Parameters
6.6.1 The Profile Method
6.6.2 The Energy Budget Method
6.6.3 Surface Roughness Length
6.6.4 Guidance for Measurements in the Surface Layer
6.7 Use of Airport Data
6.8 Treatment of Missing Data
6.8.1 Substitution Procedures
6.9 Recommendations











